The Interwar Period was a tumultuous era between World War I and World War II marked by political instability, economic crises, and the rise of totalitarian regimes.
The Weimar Republic (1919-1933) Explained
The Weimar Republic was a short-lived democratic government in Germany that faced political instability, economic crisis, and ultimately paved the way for the rise of the Nazi Party.
The Treaty of Versailles (1919) Explained
The Treaty of Versailles was a peace treaty signed after World War I that imposed harsh conditions on Germany, leading to resentment and contributing to the outbreak of World War II.
The Assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand (1914) Explained
The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand triggered the start of World War I.
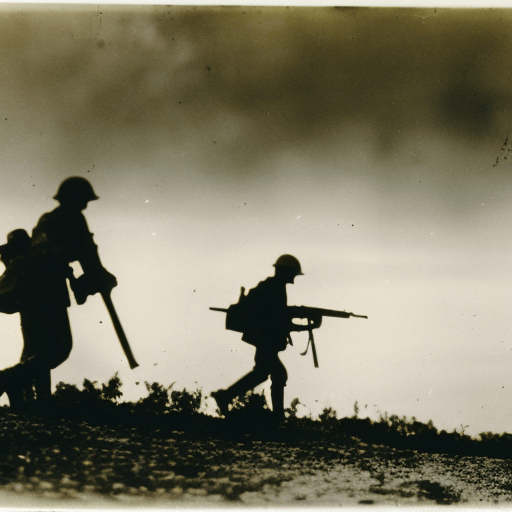
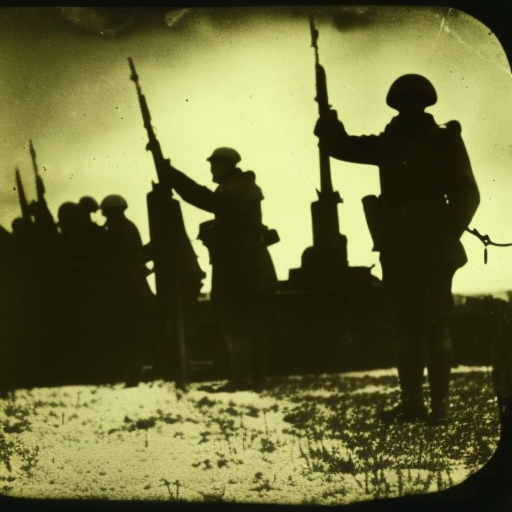
World War I (1914-1918) Explained
World War I was a global conflict fought between 1914 and 1918, involving major powers and resulting in significant political, social, and economic changes.
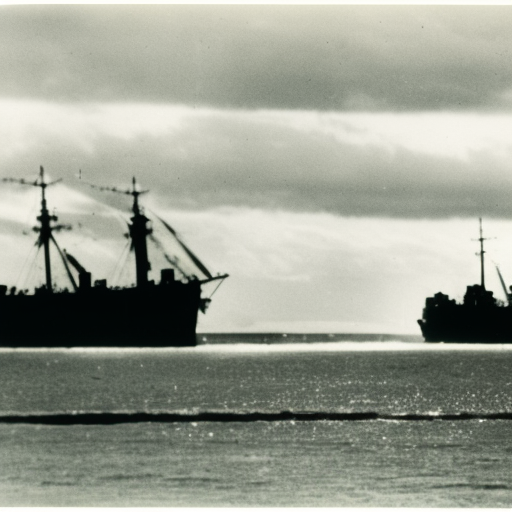
Scuttling of the German fleet at Scapa Flow Explained
The scuttling of the German fleet at Scapa Flow was the deliberate sinking of the German High Seas Fleet by its own sailors at the end of World War I.
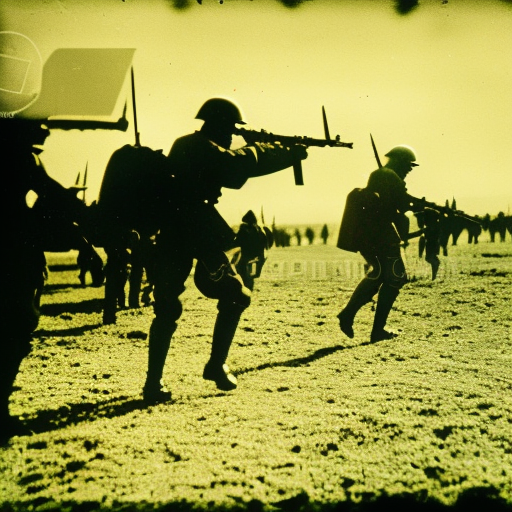
World War I Explained
World War I was a global conflict that lasted from 1914 to 1918, involving major powers and resulting in significant political, social, and economic changes.
German Revolution of 1918–1919 Explained
The German Revolution of 1918-1919 was a period of political upheaval and social unrest that led to the end of the German monarchy and the establishment of the Weimar Republic.
Armistice of 11 November 1918 Explained
The Armistice of 11 November 1918 marked the end of World War I, bringing a ceasefire and peace negotiations between the Allies and Germany.
Armistice Day Explained
Armistice Day commemorates the end of World War I and honors the sacrifices of military personnel.
Interwar period Explained
The interwar period refers to the time between World War I and World War II, characterized by political instability, economic depression, and the rise of totalitarian regimes.