The Gothic Architectural Movement
The Gothic architectural movement was a significant development in European architecture that emerged in the late 12th century and lasted until the 16th century. It originated in France and spread throughout Europe, leaving a lasting impact on the design and construction of cathedrals, churches, and other religious buildings. The movement was characterized by its distinctive features, including pointed arches, ribbed vaults, flying buttresses, and large stained glass windows.
Origins and Influences
The Gothic architectural movement was a direct response to the Romanesque style that dominated Europe during the early Middle Ages. The Romanesque style was characterized by thick walls, small windows, and rounded arches. However, as Europe experienced economic and cultural growth during the High Middle Ages, architects sought to create grander and more awe-inspiring structures.
The Gothic style drew inspiration from various sources, including the Romanesque architecture of the past, as well as Islamic and Byzantine influences. The pointed arch, a defining feature of Gothic architecture, was borrowed from Islamic architecture. The use of ribbed vaults and flying buttresses allowed for taller and more spacious interiors, while stained glass windows added a sense of ethereal beauty and spirituality.
Key Features of Gothic Architecture
Gothic architecture is characterized by several key features that distinguish it from other architectural styles. These features include:
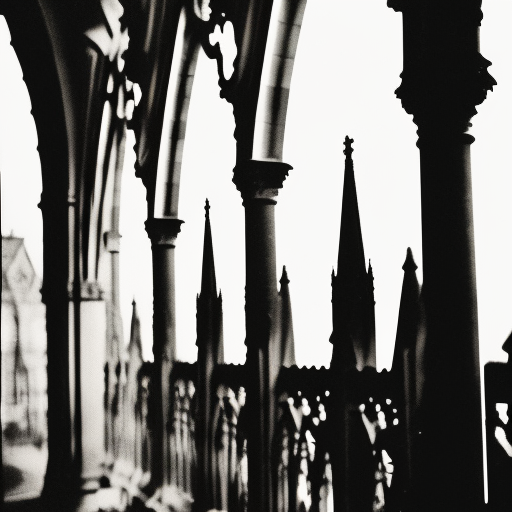
1. Pointed Arches: Gothic architecture is known for its pointed arches, which replaced the rounded arches of the Romanesque style. Pointed arches allowed for greater height and created a sense of upward movement.
2. Ribbed Vaults: Ribbed vaults were used to support the weight of the roof and distribute it evenly, allowing for larger and more open interior spaces. The ribs also added a decorative element to the ceilings.
3. Flying Buttresses: Flying buttresses were external supports that transferred the weight of the vaulted ceilings to the walls, allowing for thinner walls and larger windows. They also added an aesthetic element to the exterior of the buildings.
4. Stained Glass Windows: Gothic architecture is renowned for its large stained glass windows, which were not only decorative but also served as a way to transmit light into the interior of the buildings. These windows often depicted biblical scenes and stories.
Examples of Gothic Architecture
Some of the most famous examples of Gothic architecture include:
- Notre-Dame Cathedral (Paris, France): One of the most iconic Gothic cathedrals, Notre-Dame is known for its elaborate rose windows, flying buttresses, and intricate sculptures.
- Chartres Cathedral (Chartres, France): Chartres Cathedral is renowned for its stunning stained glass windows, particularly the Blue Virgin window.
- Westminster Abbey (London, England): Westminster Abbey is a prime example of English Gothic architecture, with its pointed arches, ribbed vaults, and intricate stone carvings.
- Cologne Cathedral (Cologne, Germany): Cologne Cathedral is one of the largest Gothic cathedrals in the world and is famous for its twin spires and intricate facade.
Legacy and Influence
The Gothic architectural movement had a profound and lasting influence on European architecture. Its emphasis on height, light, and grandeur transformed the way buildings were designed and constructed. The Gothic style also extended beyond religious buildings and influenced the design of castles, palaces, and civic structures.
The legacy of Gothic architecture can still be seen today in the numerous cathedrals and churches that dot the European landscape. Its influence can also be seen in later architectural movements, such as the Gothic Revival in the 19th century.
In conclusion, the Gothic architectural movement was a transformative period in European architecture, characterized by its pointed arches, ribbed vaults, flying buttresses, and stained glass windows. It emerged as a response to the Romanesque style and drew inspiration from various sources. The Gothic style left a lasting legacy and continues to inspire awe and admiration for its grandeur and beauty.