Summary: Medical devices play a crucial role in the diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring of various medical conditions. They encompass a wide range of instruments, machines, implants, and software that are designed to improve patient care and outcomes. From simple devices like thermometers and blood pressure monitors to complex technologies like pacemakers and robotic surgical systems, medical devices have revolutionized healthcare. They are subject to strict regulations to ensure safety and efficacy, and their development continues to advance with the integration of artificial intelligence and other cutting-edge technologies.
Types of Medical Devices
Medical devices can be categorized into several types based on their function and purpose. Diagnostic devices, such as X-ray machines, ultrasound scanners, and blood glucose monitors, are used to identify and monitor medical conditions. Therapeutic devices, like pacemakers, insulin pumps, and prosthetic limbs, are designed to treat or manage diseases. Surgical instruments, including scalpels, forceps, and sutures, are used during surgical procedures. Implantable devices, such as artificial joints and cardiac stents, are permanently placed inside the body to replace or support damaged organs or tissues.
Regulation and Safety
Medical devices are subject to rigorous regulations to ensure their safety, effectiveness, and quality. In many countries, regulatory bodies like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) oversee the approval and monitoring of medical devices. These agencies evaluate the devices’ design, manufacturing processes, and clinical data before granting market clearance or approval. Post-market surveillance is also conducted to monitor the devices’ performance and identify any potential risks or issues.
Advancements in Medical Devices
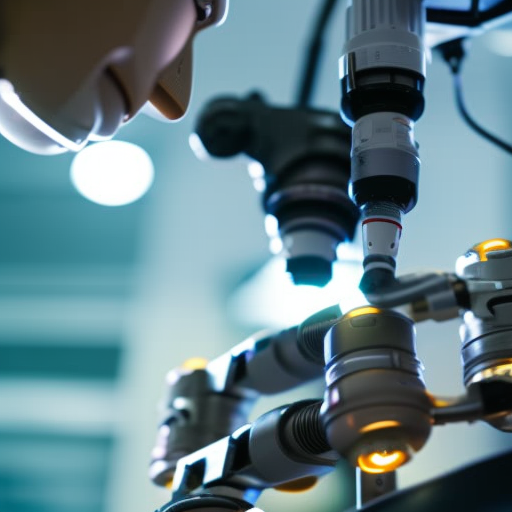
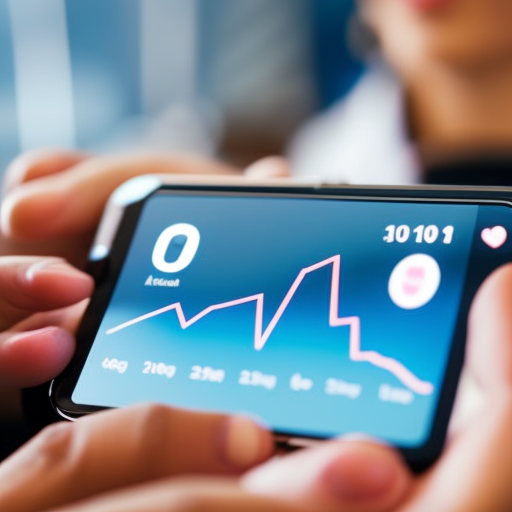
Advancements in technology have led to significant improvements in medical devices. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms has enhanced the capabilities of devices, allowing for more accurate diagnoses and personalized treatments. For example, AI-powered imaging systems can analyze medical images and detect abnormalities with high precision. Robotic surgical systems enable surgeons to perform complex procedures with enhanced precision and control. Wearable devices, such as fitness trackers and smartwatches, have also gained popularity in recent years, allowing individuals to monitor their health and fitness levels.
Challenges and Future Trends
Despite the numerous benefits of medical devices, there are challenges that need to be addressed. Cybersecurity is a growing concern, as interconnected devices can be vulnerable to hacking and data breaches. Additionally, the high cost of some medical devices can limit their accessibility, particularly in developing countries. Efforts are being made to address these challenges and make medical devices more affordable and accessible.
Looking ahead, the future of medical devices holds great promise. The integration of AI, robotics, and nanotechnology is expected to revolutionize healthcare. AI algorithms will continue to improve diagnostic accuracy, while robotic systems will enable more precise and minimally invasive surgeries. Nanotechnology will allow for the development of smaller, more efficient devices that can target specific areas within the body. Furthermore, the rise of telemedicine and remote patient monitoring will further enhance the use of medical devices, allowing for more efficient and convenient healthcare delivery.
In conclusion, medical devices are essential tools in modern healthcare. They encompass a wide range of instruments, machines, implants, and software that aid in diagnosis, treatment, and monitoring. Strict regulations ensure their safety and efficacy, and advancements in technology continue to drive innovation in this field. With the integration of AI, robotics, and nanotechnology, the future of medical devices looks promising, offering improved patient care and outcomes.